In today’s corporate landscape, environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors have become integral to business success. Companies that embrace ESG reporting not only demonstrate their commitment to sustainable innovation practices but also build trust with stakeholders. This guide explores the best practices and benefits of ESG reporting, providing a comprehensive overview for businesses looking to enhance their ESG strategies.
What is ESG Reporting?

ESG reporting standards are a disclosure process where companies communicate their performance and impact concerning environmental, social, and governance issues. This type of reporting helps businesses transparently share their efforts and outcomes in these areas, providing stakeholders with valuable insights into their sustainable practices and long-term viability.
ESG reporting goes beyond traditional financial reporting, offering a holistic view of a company’s operations and its impact on the world. However, this transparency is critical in building trust and accountability with investors, customers, employees, and the broader community.
What Does ESG Stand For?
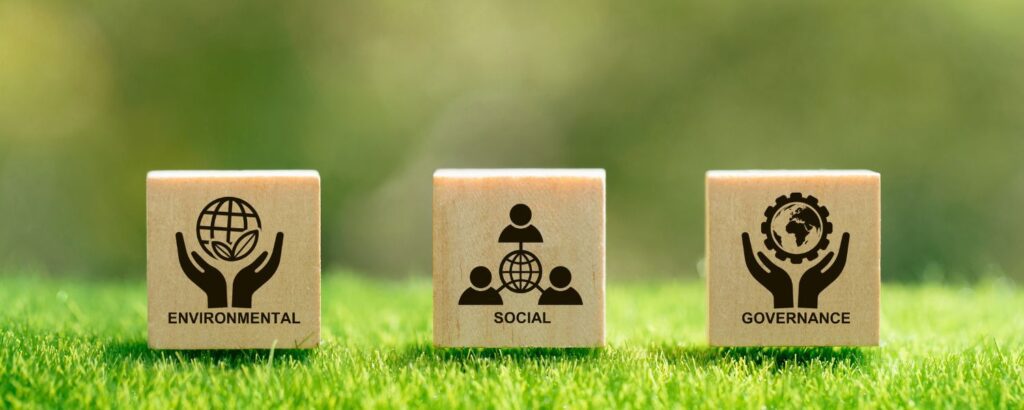

1. Environmental
This component focuses on a company’s impact on the planet. It includes aspects such as carbon emissions, energy consumption, waste management, water usage, and biodiversity conservation. Environmental reporting aims to showcase efforts toward reducing the ecological footprint and promoting environmental sustainability.
2. Social
The social aspect covers how a company manages relationships with employees, suppliers, customers, and the communities in which it operates. Key areas include labour practices, human rights, community engagement, diversity and inclusion, and health and safety. Reporting on social factors highlights a company’s commitment to ethical practices and social responsibility.
3. Governance
Governance involves the internal systems and processes that control and direct the company. It includes topics like board composition, executive compensation, shareholder rights, risk management, and transparency. Effective governance ensures that a company operates with integrity and accountability, fostering long-term success.
Why ESG Reporting is Important

ESG reporting is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it enhances transparency and accountability, allowing stakeholders to make informed decisions. Investors, in particular, use ESG data to assess the long-term sustainability and ethical standards of a company, which can influence investment choices.
Secondly, ESG reporting can lead to improved operational efficiencies and cost savings. By identifying areas for improvement in environmental and social practices, companies can reduce waste, enhance energy efficiency, and improve employee satisfaction.
Furthermore, ESG reporting helps companies meet regulatory requirements and align with industry standards. As ESG issues gain prominence globally, governments and regulatory bodies are increasingly mandating disclosure of ESG practices. However, to these requirements is essential for legal compliance and maintaining a positive reputation.
Finally, effective ESG reporting can enhance a company’s brand image and competitive advantage. Moreover, consumers and clients are more likely to support businesses that are committed to sustainability and ethical practices, fostering loyalty and trust.
Benefits of ESG Reporting

1. Enhanced Investor Relations
Investors are increasingly prioritizing ESG factors in their decision-making processes. By providing comprehensive ESG reports, companies can attract responsible investors who seek sustainable and ethical investment opportunities. This can lead to a more stable and diversified investor base.
2. Improved Risk Management
ESG reporting helps companies identify and mitigate risks related to environmental, social, and governance issues. By understanding potential vulnerabilities and implementing proactive measures, businesses can protect themselves from future disruptions and enhance their resilience.
3. Operational Efficiency
Detailed ESG reporting can uncover inefficiencies and areas for improvement within a company. Businesses can streamline operations, reduce costs, and boost overall performance by addressing these issues. For example, reducing energy consumption benefits the environment and lowers utility expenses.
4. Regulatory Compliance
With the increasing focus on ESG issues, regulatory bodies are imposing stricter reporting requirements. Comprehensive ESG reporting ensures that companies comply with these regulations, avoid legal penalties, and maintain their license to operate.
5. Enhanced Reputation and Brand Value
Companies that excel in ESG reporting are viewed more favourably by consumers, employees, and the broader community. This positive perception can enhance brand reputation, attract top talent, and foster customer loyalty. A strong ESG profile differentiates a company from its competitors and positions it as a leader in sustainability.
What are ESG Reporting Frameworks?

ESG reporting frameworks provide standardized guidelines for companies to report on their natural, social, and governance practices. These frameworks help ensure consistency, comparability, and transparency in ESG disclosures. Further, some of the most widely recognized ESG reporting frameworks include:
1. Global Reporting Initiative (GRI)
The GRI framework is one of the most largely used standards for sustainability reporting. It provides comprehensive guidelines for reporting on a wide range of ESG topics, including environmental impact, labor practices, human rights, and governance.
2. Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB)
SASB focuses on financially material ESG factors that are relevant to specific industries. It provides industry-specific standards that help companies disclose ESG information that is most pertinent to their business and investors.
3. Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures
The TFCRFD framework focuses on climate-related risks and opportunities. It provides recommendations for companies to disclose information on how they are managing climate-related risks and incorporating these considerations into their financial planning.
4. Integrated Reporting (IR)
The IR framework aims to provide a holistic view of a company’s strategy, governance, performance, and prospects. It integrates financial and non-financial information to demonstrate how a company creates value over time.
Best Practices for ESG Reporting

1. Define Clear Objectives
Before embarking on ESG reporting, companies should define clear objectives and goals. Understanding what they aim to achieve with corporate social respnsibilty helps in creating focused and meaningful reports. Objectives include improving transparency, attracting investors, or enhancing brand reputation.
2. Engage Stakeholders
Engaging with stakeholders, including investors, employees, customers, and communities, is crucial for effective ESG reporting. Stakeholder input helps companies understand what information is most valuable and relevant. However, it also demonstrates a commitment to transparency and accountability.
3. Use Reliable Data
Accurate and reliable data is the backbone of credible ESG reporting. Companies should implement robust data collection and management systems to ensure the integrity of their ESG information. This includes using verified data sources and third-party audits when necessary.
4. Align with Recognized Frameworks
Aligning ESG reports with recognized frameworks such as GRI, SASB, TCFD, or IR enhances the credibility and comparability of the information disclosed. These frameworks provide standardized guidelines that help companies report consistently and transparently.
5. Regular Reporting
Regular and consistent governance is essential for tracking progress and demonstrating a commitment to sustainability. Companies should establish a reporting schedule, whether annual or semi-annual, and stick to it. Regular updates keep stakeholders informed and engaged.
6. Transparency and Honesty
Transparency and honesty are fundamental principles of effective socal . Companies should openly disclose both positive and negative impacts, challenges, and areas for improvement. This builds trust with stakeholders and shows a genuine commitment to continuous improvement.
7. Continuous Improvement
ESG reporting is not a one-time exercise but a continuous process. Companies should regularly review and update their ESG strategies and reporting practices to reflect evolving standards, stakeholder expectations, and business priorities.
Challenges and Solutions in ESG Reporting

A. Data Collection and Management
1. Challenge: Collecting and managing vast amounts of ESG data can be complex and resource-intensive.
2. Solution: Implementing ESG reporting software and ESG reporting tools can streamline data collection and management. These solutions automate data gathering, ensure accuracy, and simplify the reporting process.
B. Standardization
1. Challenge: The need for more standardization in socio economics can make it difficult to compare and benchmark performance across companies.
2. Solution: Adopting widely recognized ESG reporting frameworks and standards, such as GRI or SASB, helps ensure consistency and comparability. Companies should also engage in industry collaborations to promote standardization.
C. Stakeholder Engagement
1. Challenge: Engaging diverse stakeholders with varying interests and priorities can be challenging.
2. Solution: Companies should adopt a structured stakeholder engagement approach. This involves identifying key stakeholders, understanding their concerns, and incorporating their feedback into social reporting practices.
D. Balancing Transparency and Competitiveness
1. Challenge: Companies may fear disclosing certain ESG information could compromise their competitive position.
2. Solution: While transparency is crucial, companies should carefully evaluate the sensitivity of the information they disclose. Balancing openness with strategic discretion ensures that critical insights are shared without compromising competitiveness.
E. Keeping Up with Regulatory Changes
1. Challenge: Rational sustainability requirements are evolving rapidly, making it challenging for companies to stay compliant.
2. Solution: Companies should stay informed about regulatory developments and engage with industry associations and regulatory bodies. Regularly updating reporting practices and seeking expert advice can ensure compliance with changing requirements.
Conclusion
Environmental is a vital practice for modern businesses aiming to build trust, transparency, and long-term sustainability. Furthermore, by adopting best practices and addressing common challenges, companies can enhance their social and unlock numerous benefits, including improved investor relations, operational efficiency, and brand reputation. As the importance of ESG continues to grow, companies that prioritize effective VectorGlobe social responsiabilty will be well-positioned to thrive in an increasingly conscious and responsible sustainable innovation.